The Science Behind LuViva
Biophotonics is the science of harnessing light to image, detects and manipulate biological materials.
The LuViva® Advanced Cervical Scan is based on the science of biophotonics. LuViva scans cervical tissue with light and detect chemical and structural changes at the cellular level.
Unlike the Pap Smear, Liquid-based cytology or biopsy LuViva is designed to provide a result immediately after the scan with no waiting for laboratory reports.
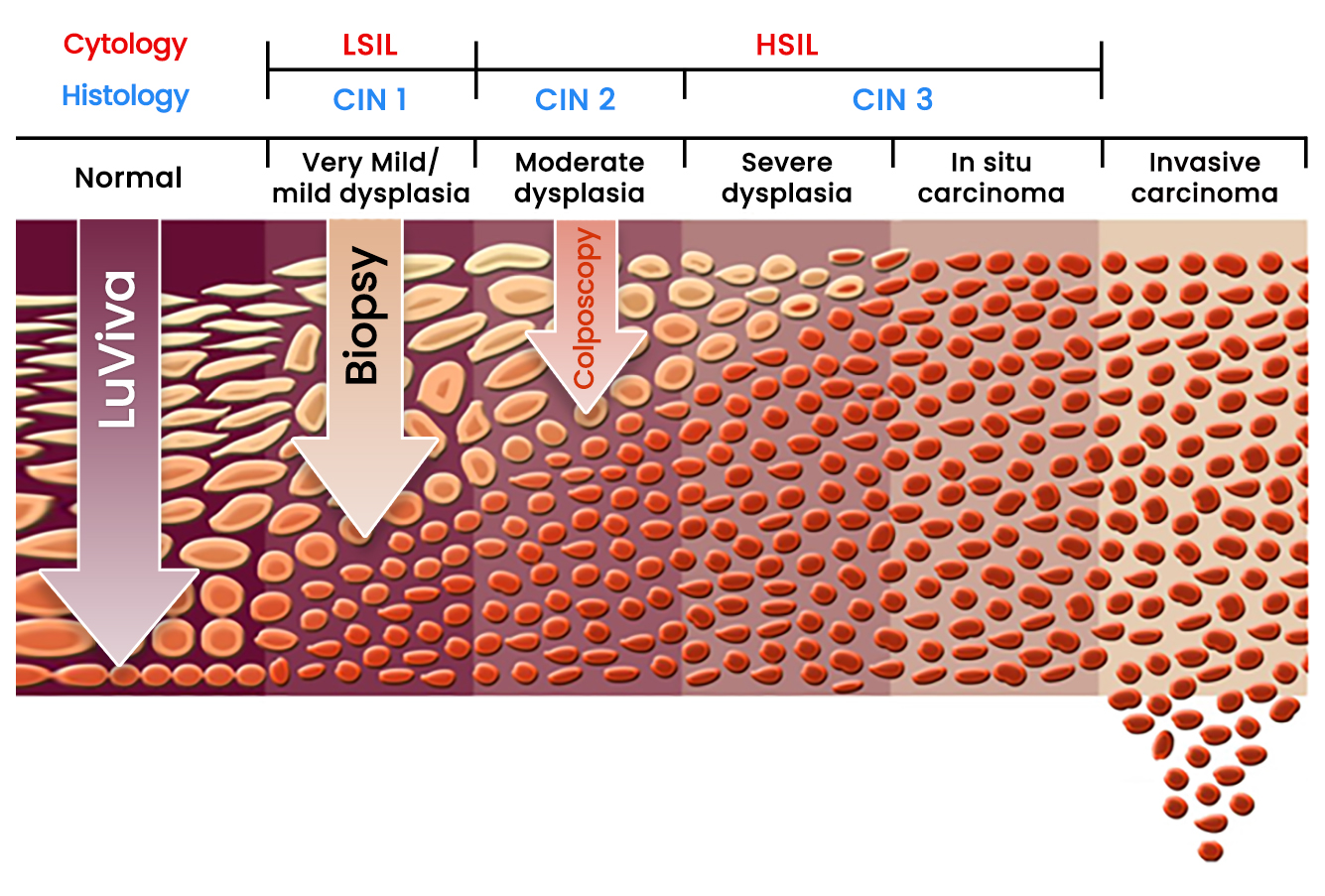
Since the scanning technology can detect chemical and physical changes below the surface, the disease may be detected before it reaches the surface and be detected by colposcopy.
Biophotonics can detect diseases before they become apparent on the surface.
Multimodal hyperspectroscopy
The LuViva® Advanced Cervical Scan uses reflectance and fluorescence spectroscopy in vivo to detect both physical and chemical changes in the cervical tissue that are indicators of cervical cancer.
Reflectance
Reflectance spectroscopy measures the color and intensity of reflected light and can be used to determine if structural changes are taking place in tissue. In the case of LuViva, structural changes that effect light reflectance are: epithelial thickening, nuclear size and content and increased blood flow.
Fluorescence
Fluorescence spectroscopy measures the wavelength of light that is re-emitted from an object that has been illuminated. It is used to determine the presence and concentration of certain chemical markers present in tissue. In the case of LuViva, fluorescent markers present that may indicate the early stages of cancer are: tryptophan, flavins and/or collagen.
LuViva’s performance in pivotal clinical trial
- Detected disease up to 2 years earlier than Pap, HPV, and colposcopy
- May reduce unnecessary colposcopy and biopsies by as much as 40%
- Detected 36.4% more CIN2+ than tests used under current guidelines
Source: Twiggs LB, Chakhtoura NA, Ferris DG, et al. Multimodal hyperspectroscopy as a triage test for cervical neoplasia: pivotal clinical trial results. Gynecol Oncol. 2013;130(1):147-151.
Studies and conclusions
Leo B. Twiggs MD
Professor Emeritus Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Miami Miami, Florida, USA
„LuViva has shown the ability to reduce unnecessary procedures by 35–40%, thus significantly reducing health care expenditures in the field of cervical precancer and improving the patient’s experience.”
Source: Pub 2013 Is Colposcopy and-or Biopsy Always Necessary
Zoárd T. Krasznai MD
Associate Professor
Director of Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinic University of Debrecen
Debrecen, Hungary
„In the case of cytological abnormality, the Multimodal Hyper Spectroscopy (MHS) provides an immediate result based on advanced digital technology, and because of its outstanding false negative rate it is a great aid and should be considered in the triage of such patients.”
Source: Pub 2021 MHS- The Use of Digital Technology in Cervical Cancer Screening
Daron G. Ferris MD
Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
GRU Cancer Center
Augusta, Georgia, USA
„Use of Fluorescent and Reflective Spectroscopy (FRS) as a colposcopic adjunct was supported very favorably by women. Fewer women supported FRS replacing Pap smears. These high rates of approval by women should help the implementation of FRS technology.”
Source: Pub 2021 MHS- The Use of Digital Technology in Cervical Cancer Screening
Ömer Demir MD
Doctor of Medicine Gynecology and Obstetrics Department
Istanbul Univerity
Istanbul, Turkey
„Scanning of the cervix by Multimodal Hyper Spectroscopy (MHS) may perform similar to Pap smear + HPV testing and may have a higher specificity in low-risk pregnant women.”
Source: Pub 2020 Performance of MHS for Scanning Cervix in Pregnant Women
Publications
For more information regarding the clinical performance of LuViva® Advanced Cervical Scan, please visit this page:
Indications for LuViva
LuViva is intended for use on women aged 16+
- as a primary screener when conventional screening tests are not as available.
- who have been referred for additional testing after abnormal cytology and/or positive HPV findings and/or other risk factors prior to colposcopy and biopsy



